Angiography
Angiography: A Comprehensive Look at Heart and Vascular Imaging

Angiography
This test is similar to a traditional coronary angiogramthat uses X-rays but the dye is injected into a small vein in your arm rather than an artery in your groin. A CT coronary angiogram is not as good as a traditional coronary angiogram at detecting narrowing of small coronary arteries.
Coronary Angiography
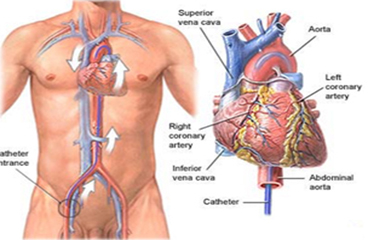
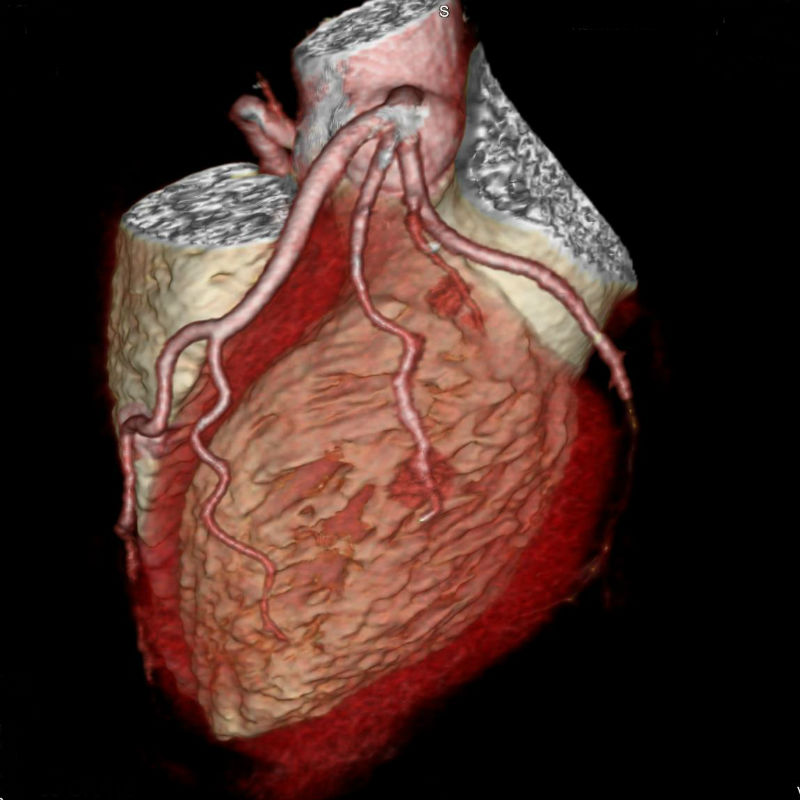
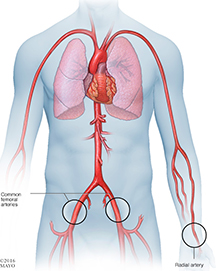
Coronary angiography is a specialised X-ray test to find out detailed information about your heart (coronary) arteries. It is mainly used if you have angina, to assess which if any of the arteries are blocked, and how severely the arteries are blocked. It involves a procedure calledcatheterisation.Coronary angiography is a special X-ray of the heart (coronary) arteries.Coronary arteries do not show up on a plain X-ray. With coronary angiography, dye is injected down the coronary arteries.
The arteries and their smaller branches then show up clearly on an X-ray ‘like a road map’. Dye is injected into the coronary arteries by using a catheter. (A catheter is a thin, flexible, hollow tube.) How this is done is described below.Therefore, coronary angiography can show the exact site and severity of any narrowing of the coronary arteries. This helps the doctor to decide on what treatment you may need. For example, if the narrowing is mild and does not need surgery; or, if the narrowing is severe and you should have a coronary artery bypass graft or coronary angioplasty.
Benefits-Heart and Vascular CT Angiography
- Heart and vascular CT angiography may eliminate the need for surgery. If surgery remains necessary, it can be performed more accurately.
- Heart and vascular CT angiography can detect narrowing or obstruction of blood vessels allowing for potentially corrective therapy to be done.
- CT angiography may give more precise anatomical detail than other imaging, particularly in small blood vessels.
- Many patients can undergo heart and vascular CT angiography to diagnose blood vessel problems.
- Heart and vascular CT angiography is faster, non-invasive and has fewer complications.
- CT Angiography is a useful way of detecting arterial (such as narrowing of blood vessels in the heart) and venous disease, as well as structural abnormalities of the heart before there are symptoms or when symptoms are not clearly related to blood vessel disease.
- There is also potentially less discomfort because contrast material is injected into an arm vein.
- No radiation remains in a patient’s body after heart and vascular CT angiography.
- X-rays used in standard CT scans have no immediate side effects
